

When diving, the pressure differences needed to cause the barotrauma come from two sources: Pulmonary barotrauma may also be caused by explosive decompression of a pressurised aircraft. The problem only arises if a breath of compressed gas is taken at depth, which will then expand on ascent to more than the lung volume.
#Otitic barotrauma treatment skin
This does not affect breath-hold skin divers as they bring a lungfull of air with them from the surface, which merely re-expands safely to near its original volume on ascent. The lungs do not sense pain when over-expanded giving the diver little warning to prevent the injury. The compressed gas in the lungs expands as the ambient pressure decreases causing the lungs to over expand and rupture unless the diver breathes out.
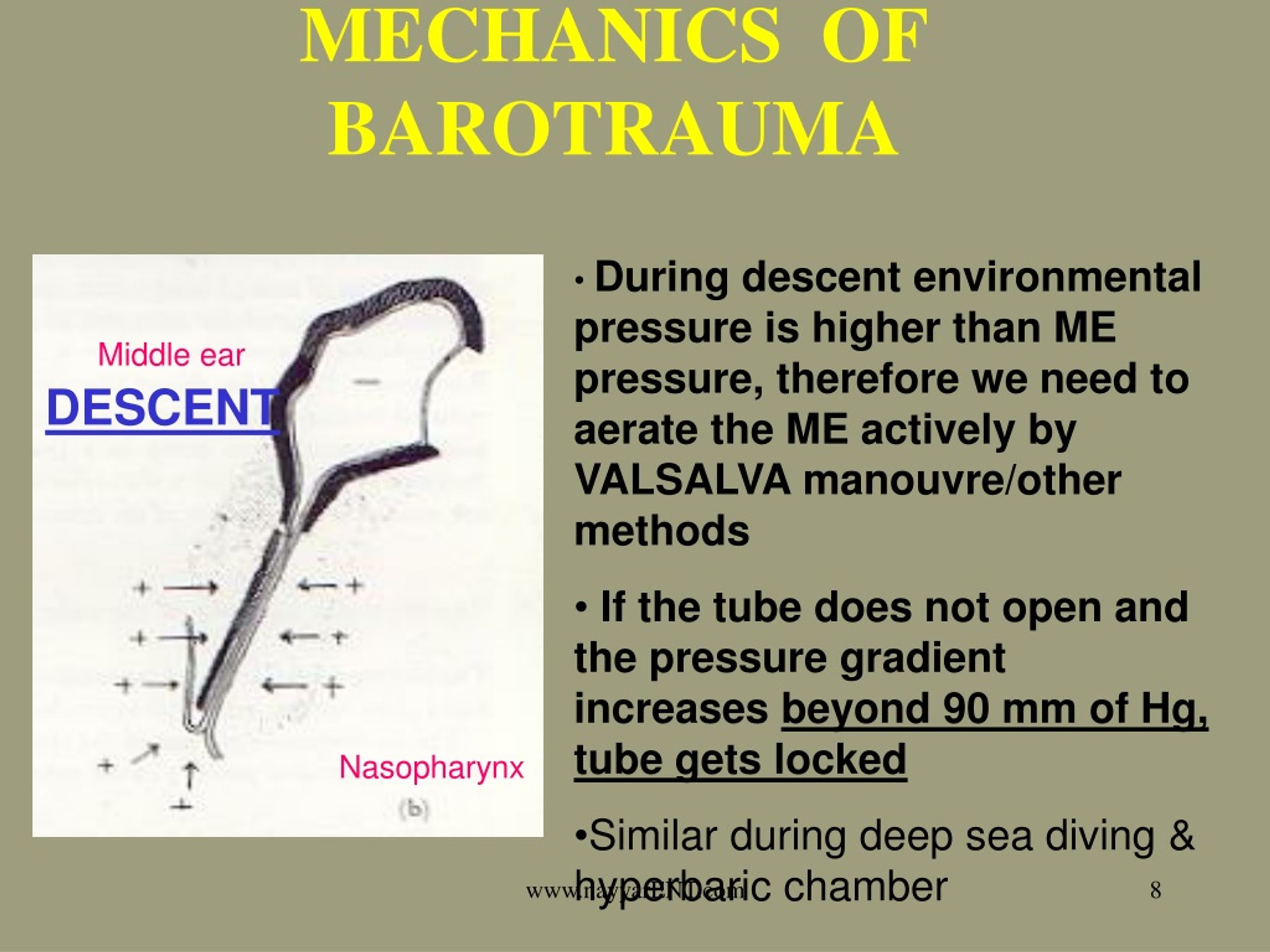
Pulmonary (lung) pressure damage in scuba divers is usually caused by breath-holding on ascent. If a diver's mask is not equalized during descent the relative negative pressure can produce petechial hemorrhages in the area covered by the mask along with subconjunctival hemorrhages. This can result in pain as well as epistaxis. The sinuses similar to other air filled cavities are susceptible to barotrauma if their openings become obstructed. Mechanical trauma to the inner ear can lead to varying degrees of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss as well as vertigo. Inner ear barotrauma (IEBT) though much less common than MEBT shares a similar mechanism. External ear barotrauma may occur on ascent if high pressure air is trapped in the external auditory canal either by tight fitting SCUBA equipment or ear wax. Middle ear barotrauma (MEBT) is the most common being experienced by between 10% and 30% of divers and is due to insufficient equilibration of the middle ear.

barometric pressure related dental pain, or dental fractures )īarotrauma can affect the external, middle, or inner ear. bone (bone necrosis and temporal lobe injury).skin (when wearing a diving suit which creates an air space).eyes (the unsupportive air space is inside the diving mask ).paranasal sinuses (causing Aerosinusitis).During decreases in ambient pressure, the higher pressure of the gas inside the air spaces causes damage to the surrounding tissues if that gas becomes trapped.Įxamples of organs or tissues easily damaged by barotrauma are: During increases in ambient pressure, the internal air space provides the surrounding tissues with little support to resist the higher external pressure. Boyle's law defines the relationship between the volume of the air space and the ambient pressure.ĭamage occurs in the tissues around the body's air spaces because gases are compressible and the tissues are not.

īarotrauma typically occurs to air spaces within a body when that body moves to or from a higher pressure environment, such as when a SCUBA diver, a free-diving diver or an airplane passenger ascends or descends, or during uncontrolled decompression of a pressure vessel. In addition to humans, and in contrast with Avian lungs, bats suffer fatal barotrauma around wind farms. Barotrauma is physical damage to body tissues caused by a difference in pressure between an air space inside or beside the body and the surrounding fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
